Vaccine-Preventable Diseases?
Vaccines protect communities by preventing diseases, ensuring healthier futures and reducing illness and suffering.
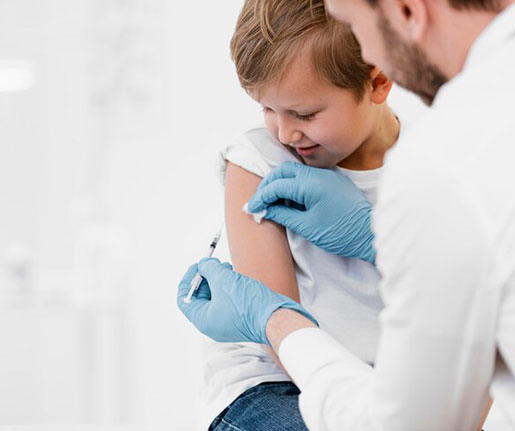
Vaccine-preventable diseases are illnesses that can be effectively prevented through vaccination. These diseases can range from mild to severe, and some can lead to significant health complications or even death. Vaccinations work by stimulating the immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens, thereby preventing infection and the spread of disease.
Symptoms: High fever, cough, runny nose, and a characteristic rash that usually starts on the face and spreads.
Complications: Serious complications can include pneumonia, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), and death. Measles can also lead to long-term health issues.
Vaccine: The MMR (Measles, Mumps, Rubella) vaccine is highly effective at preventing measles. It is typically administered in two doses, starting at 12-15 months of age.
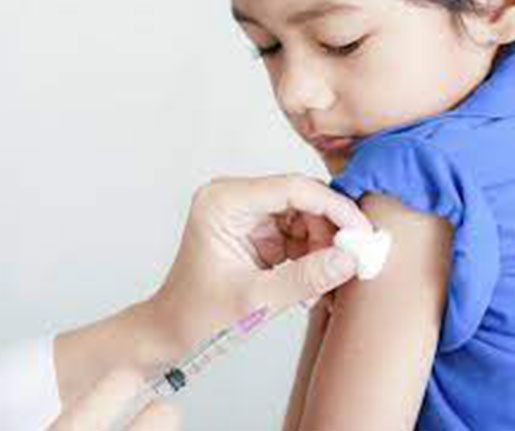

Symptoms: Severe, persistent cough that can cause fits of coughing followed by a "whooping" sound. Infants may experience difficulty breathing.
Complications: Can lead to severe respiratory issues, hospitalization, and even death, especially in infants and young children.
Vaccine: The Tdap (Tetanus, Diphtheria, Pertussis) vaccine protects against whooping cough. It is recommended for pregnant women, infants, and adolescents.
Symptoms: Early symptoms may include fever, sore throat, and fatigue. Severe cases can lead to paralysis, affecting the ability to move limbs or breathe.
Complications: Can cause permanent paralysis and, in some cases, death. The disease has been nearly eradicated globally due to effective vaccination efforts.
Vaccine: The IPV (Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine) is used to prevent polio. It is administered in multiple doses during early childhood.
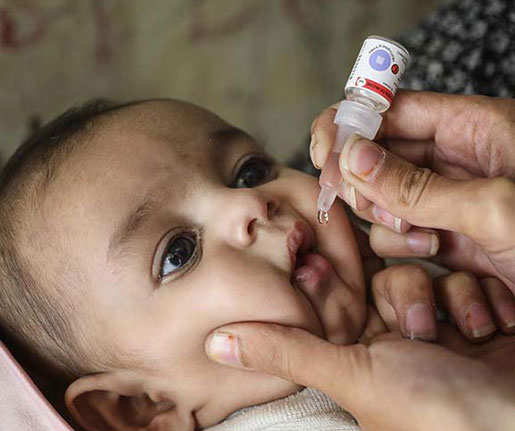
Symptoms: Fatigue, abdominal pain, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), and loss of appetite. Chronic infection can lead to liver disease.
Complications: Long-term complications include chronic liver disease, liver cancer, and liver failure.
Vaccine: The Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for all infants, children, and adults at risk of infection. It is given in a series of three or four doses.
Symptoms: Fever, cough, sore throat, muscle aches, and fatigue. Seasonal flu can lead to severe respiratory illness.
Complications: Can cause complications such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinus infections, particularly in the elderly, young children, and those with chronic health conditions.
Vaccine: The seasonal influenza vaccine is updated annually to protect against the most common flu strains and is recommended for everyone six months and older.
Symptoms: Cough, fever, difficulty breathing, and chest pain. Pneumonia can be particularly dangerous for young children and older adults.
Complications: Serious complications can include respiratory failure, sepsis, and death.
Vaccine: Pneumococcal vaccines (PCV13 and PPSV23) protect against pneumococcal diseases, including pneumonia and meningitis.
Symptoms: Severe diarrhea, vomiting, and fever. Rotavirus is a leading cause of gastroenteritis in infants and young children.
Complications: Can lead to severe dehydration, which may require hospitalization.
Vaccine: The rotavirus vaccine is given in multiple doses starting at 2 months of age, significantly reducing the risk of severe rotavirus disease.
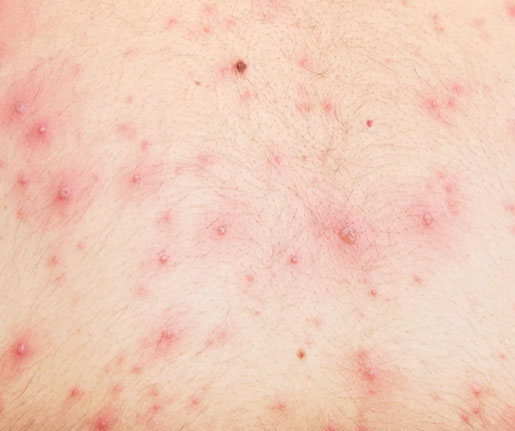
Symptoms: Itchy rash with red spots and blisters, fever, and fatigue.
Complications: Can lead to serious skin infections, pneumonia, and encephalitis. The disease can be more severe in adults and infants.
Vaccine: The varicella vaccine prevents chickenpox and is typically administered in two doses starting at 12-15 months of age.
Preventing Disease: Vaccines prevent the onset of diseases that can cause severe health problems, hospitalizations, and deaths.
Protecting the Community: Widespread vaccination helps create herd immunity, reducing the spread of diseases and protecting those who cannot be vaccinated, such as newborns and individuals with certain medical conditions.
Reducing Healthcare Costs: Preventing diseases through vaccination can reduce the burden on healthcare systems and lower overall treatment costs.
Follow Vaccination Schedules: Adhere to recommended vaccination schedules for infants, children, adults, and seniors. Your healthcare provider will offer guidance based on age, health status, and risk factors.
Consult Healthcare Providers: Regularly discuss vaccination needs with your healthcare provider to ensure that you and your family are up-to-date with necessary vaccines.
Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest information on vaccines and disease prevention through trusted sources like the CDC and WHO.

Call us if you have any problems.